Just in recent years, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) has emerged as a groundbreaking treatment option for individuals struggling with PTSD. This non-invasive therapy uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain, helping to rewire neural pathways disrupted by trauma. As you explore the benefits of TMS, you’ll discover how it can potentially alleviate your symptoms, offering hope and healing through innovative science. Understanding the mechanisms behind TMS can empower you to make informed decisions about your mental health and recovery journey.
Key Takeaways:
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive therapy that uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain, particularly targeting areas affected by trauma.
- Rewiring the brain through TMS can lead to reductions in PTSD symptoms by altering neural pathways, thereby improving mood and emotional regulation.
- Clinical studies have shown promising results for TMS in treating PTSD, suggesting it may be an effective alternative for those who have not responded to traditional therapies.
Understanding PTSD
To grasp the significance of TMS (Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation) in the context of PTSD (Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder), it is necessary to first understand what PTSD entails.
Definition of PTSD
Any exposure to a traumatic event can lead to PTSD, a mental health condition characterized by persistent and distressing symptoms that can significantly impair your daily functioning.
Symptoms of PTSD
On experiencing PTSD, you may encounter a range of symptoms that manifest in different ways, impacting your emotional and physical well-being.
For instance, you might find yourself reliving the traumatic event through flashbacks or nightmares. Hyper-vigilance and emotional numbness often accompany these experiences, making it difficult to engage in daily life or maintain relationships. Additionally, irritability and avoidance behaviors may surface, as you attempt to distance yourself from reminders of the trauma and the feelings associated with it.
Prevalence and Risk Factors
Beside the symptoms, understanding the prevalence and risk factors associated with PTSD is necessary to recognizing its impact on individuals and communities.
- Approximately 7-8% of the population is diagnosed with PTSD at some point in their lives.
- Women are more likely to develop PTSD than men, often due to the prevalence of certain types of trauma.
- Experiencing additional stressors like a history of mental health issues can increase vulnerability.
Understanding the risk factors is important because they can shape your experience of trauma and influence recovery. Factors such as genetics, prior trauma history, and the presence of a support system can all play significant roles in how you cope with PTSD. Perceiving the situation from these angles can provide insights into your healing journey.
Traditional Treatment Options
On your path to recovery, exploring traditional treatment options available for PTSD can help you regain control of your life.
Traditional methods often include psychotherapy approaches, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or prolonged exposure therapy, which work to gradually help you face and process the trauma. Medication, such as antidepressants, may also be utilized to alleviate symptoms. However, these methods may not work for everyone, highlighting the need for diversified treatment options. Traditional treatment can, at times, leave certain gaps in addressing specific aspects of PTSD, which is where innovative therapies like TMS become relevant in your healing process.
The Brain and Trauma
Any understanding of PTSD begins with recognizing how trauma can reshape your brain. Trauma can impact the way your brain functions, altering your emotional responses and cognitive processes. This effect is profound, as it directly influences how you perceive and react to the world around you.
How Trauma Affects the Brain
By experiencing trauma, your brain may become hyper-responsive to stress. This heightened state can lead to persistent feelings of anxiety, fear, and even depression, affecting your daily life and overall well-being.
Neurotransmitters and Mood Regulation
Before trauma, your brain maintains a balance of neurotransmitters that regulate mood. However, traumatic experiences can disrupt this balance, leading to emotional instability and altered mental health.
Understanding the role of neurotransmitters is imperative when discussing PTSD. They are chemical messengers that help transmit signals between neurons, influencing your mood and emotional regulation. Imbalances in these neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, can contribute significantly to the symptoms of PTSD, making it difficult for you to experience joy or maintain emotional stability.
The Role of the Amygdala
After experiencing trauma, the amygdala, the part of your brain responsible for processing emotions and fear responses, may become overactive. This overactivity can lead to heightened vigilance, making it difficult for you to feel safe even in non-threatening situations.
Trauma can significantly alter how your amygdala functions. Generally, it evaluates threats and triggers your fight-or-flight response, but with trauma, it may react even to minor stressors. This heightened sensitivity helps explain the anxiety and fear often associated with PTSD, as your brain struggles to differentiate between real danger and safety.
Changes in Brain Structure
Above all, trauma can lead to structural changes in your brain. These alterations can affect various areas, impacting how you process emotions, form memories, and interact socially.
Role changes in brain structure can occur after an individual experiences trauma. You may see a reduction in the size of areas like the hippocampus, which plays a key role in memory and learning. This can affect your ability to form new memories and recall past ones accurately. Additionally, alterations in the prefrontal cortex can impair your ability to regulate emotions and make rational decisions. These structural changes create challenges in coping with trauma and contribute to the enduring symptoms of PTSD.
Overview of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
Now, as the understanding of mental health evolves, innovative treatments like Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Post-traumatic Stress disorder have gained prominence. This non-invasive therapy uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain, potentially transforming the way trauma-related mental health issues are treated.
What is TMS?
The aim of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is to alleviate symptoms of various mental health disorders by applying magnetic pulses to specific areas of your brain. This technique is particularly beneficial for conditions like PTSD.
Mechanism of Action
Stimulation of the brain using TMS is achieved through a coil placed on the scalp, producing brief magnetic pulses. These pulses create electric currents that can influence neuronal activity, which may help in reestablishing normal brain function after trauma.
Further, TMS has been shown to modulate the excitability of neurons, either increasing or decreasing their activity based on the targeted area. This mechanism enables TMS to promote positive changes by fostering neural connections that might have been disrupted due to trauma.
Types of TMS
Behind TMS therapy, several methods exist that can tailor treatment according to individual needs. The primary types include:
| 1. Repetitive TMS (rTMS) | Delivers repeated magnetic pulses to the brain. |
| 2. Deep TMS (dTMS) | Penetrates deeper brain regions for more extensive stimulation. |
| 3. Guided TMS | Uses real-time imaging to target specific areas. |
| 4. Theta Burst Stimulation (TBS) | A faster and more efficient form of rTMS. |
| 5. Synchronized TMS | Aligns stimulation with neural rhythmic patterns. |
In addition, various factors such as the type of device used and the frequency of treatment sessions can influence the effectiveness of TMS. Recognizing the nuances in treatment allows your clinician to personalize your experience.
Effectiveness of TMS for Mental Health
Any discussion on TMS would be incomplete without addressing its effectiveness. Numerous studies have demonstrated its positive impact on mental health, especially for those grappling with PTSD symptoms.
For instance, a meta-analysis of clinical trials suggests that TMS significantly reduces PTSD symptoms and enhances overall emotional well-being. This evidence highlights not only the promise TMS holds but also its potential role as part of a broader approach to mental health treatment.
TMS for PTSD: The Science
Once again, the impact of trauma on your mental health has led researchers to explore innovative solutions. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) has emerged as a promising treatment for PTSD, leveraging magnetic fields to stimulate brain areas involved in mood regulation and trauma response.
Clinical Studies and Findings
Clinical studies have shown that TMS significantly reduces PTSD symptoms in many patients. These findings reveal that after multiple sessions, individuals often experience a marked improvement in their overall mental health, providing a beacon of hope for those suffering from the long-lasting effects of trauma.
TMS Protocols for PTSD
Findings indicate that specific TMS protocols tailored for PTSD can enhance treatment efficacy. Typically, these involve multiple sessions per week over several weeks, focusing on particular brain regions like the prefrontal cortex, which is commonly associated with emotional regulation.
Considering the variability in PTSD presentations, individualizing TMS protocols can enhance your treatment experience. Adjustments in frequency, intensity, and duration are made based on your unique symptoms, ultimately aiming for maximum therapeutic benefit while minimizing potential side effects.
Neuroplasticity and TMS
Protocols involving TMS capitalize on the brain’s neuroplasticity, promoting the reorganization of neural pathways impacted by trauma. This ability allows your brain to adapt, potentially reducing the emotional and psychological grip of traumatic memories.
Another factor to note is that neuroplasticity contributes to long-term healing. When TMS engages your brain’s natural adaptability, it may not only alleviate PTSD symptoms but also instill coping mechanisms that create more resilient mental health over time.
Long-term Benefits of TMS
Across various studies, the long-term benefits of TMS for PTSD include sustained symptom relief and improved emotional regulation. Patients often report a greater sense of well-being and a decreased reliance on medications, making it a viable option for lasting change.
Plus, the integration of TMS into your treatment plan can foster long-term improvements in your overall quality of life. Over time, this holistic approach can empower you, equipping you with the tools needed to navigate challenges related to PTSD effectively.
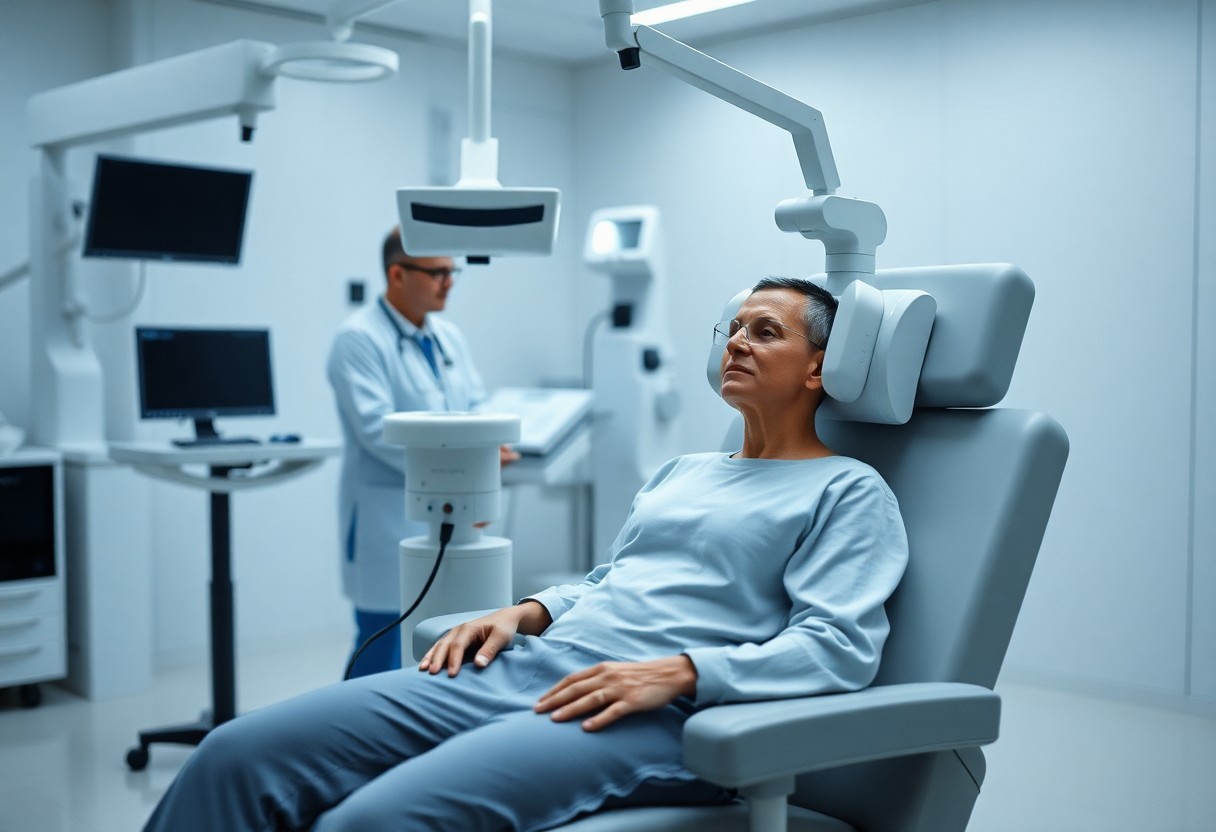
The TMS Treatment Process
All individuals seeking TMS for PTSD will first undergo a structured treatment process designed to optimize outcomes and ensure safety.
Pre-Treatment Evaluation
Before starting TMS therapy, you will participate in a thorough evaluation with your healthcare provider. This assessment will involve discussing your medical history, current symptoms, and any previous treatments you have undergone. This step is vital to determine if TMS is the right option for you and to create a tailored treatment plan that addresses your specific needs.
The TMS Session: What to Expect
Between the start of your TMS treatment and its conclusion, you can expect to attend multiple sessions. Each session typically lasts about 20 to 40 minutes, during which a specialized device will deliver magnetic pulses to targeted areas of the brain.
Further, during the TMS session, you will be seated in a comfortable chair while a magnetic coil is placed on your scalp. You may feel a tapping sensation as the machine delivers short bursts of magnetic energy. Many patients find the process relatively easy to tolerate, often describing it as a subtle sensation rather than painful.
Side Effects and Safety
Below the surface, while TMS is generally well-tolerated, some side effects may occur. You might experience mild headaches, scalp discomfort, or temporary muscle twitching at the treatment site, but these effects usually resolve quickly.
Process-wise, the safety profile of TMS is robust. Serious side effects are rare, and it is non-invasive, making it a viable option for many individuals. Your healthcare provider will monitor you closely throughout the treatment to ensure your comfort and address any concerns that may arise.
Post-Treatment Considerations
Above all, after completing your TMS sessions, it is important to remain engaged with your mental health. You may notice changes in your mood or thoughts following treatment, and open communication with your provider can help navigate this transition.
In fact, many individuals benefit from continued therapy or follow-up sessions after their TMS treatment. Engaging in support groups, counseling, or personal strategies can enhance your recovery process and ensure that you are supported as you progress on your journey to healing.
Comparing TMS with Other Treatments
Despite the variety of treatment options available for PTSD, understanding their effectiveness can empower you in making informed choices. Below is a comparison of TMS with other common treatments for PTSD:
| Treatment Type | Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| Medication | Often effective, but may have side effects and take time to adjust dosages. |
| Psychotherapy | Can be highly effective, but may require a significant time commitment. |
| TMS | Promising results with fewer side effects, offering quick treatment sessions. |
TMS vs. Medications
With various medications prescribed for PTSD, TMS presents a non-invasive alternative. While medications can alleviate symptoms, they may have unwanted side effects and often require time to find the right balance in dosage. With TMS, you can experience symptom relief without these additional concerns.
TMS vs. Psychotherapy
About psychotherapy, it involves talking through your trauma with a trained therapist, which can take months or even years. While it can provide deep insights and long-lasting benefits, some may find it challenging to verbalize their experiences. TMS, on the other hand, offers a more direct approach by targeting brain function without requiring extensive verbal exploration.
Psychotherapy helps you process your trauma and develop coping strategies, but it is not always quick. Meanwhile, TMS can stimulate the brain’s neural pathways, providing a complementary approach that may enhance the benefits of psychotherapy. Many individuals find success when combining both treatments, utilizing TMS to prime the brain for deeper therapeutic work.
Combined Treatment Approaches
Against the backdrop of diverse treatment modalities, combining TMS with psychotherapy could yield the most favorable outcomes. Each approach targets different aspects of PTSD, potentially leading to a more comprehensive recovery strategy.
Even when used together, TMS can prepare your brain for the insights gained during psychotherapy. This synergistic effect may allow you to unpack trauma more effectively, maximizing your healing journey. Healthcare professionals can help you determine if this combined approach is right for you.
Patient Testimonials
Any discussion about treatment is incomplete without considering patient experiences. Testimonials can shed light on how TMS has affected individuals like you, sharing valuable insights into its efficacy and impact.
With numerous positive accounts, many individuals express that TMS helped them reclaim their lives from the grips of PTSD. Their stories often highlight increased energy, mood improvement, and a newfound sense of hope, emphasizing how this innovative treatment can change lives for the better.
Future Directions in TMS Research
Many researchers believe that the future of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is promising, especially as it relates to addressing conditions like PTSD. As you explore options for< a href="https://www.smarttms.co.uk/post-traumatic-stress-disorder/" rel="nofollow noreferrer" target="_blank">PTSD Recovery with TMS, you’ll find that advancements in technology and ongoing clinical trials are paving the way for innovative treatments that can further enhance outcomes in mental health care.
Innovations in TMS Technology
Across the globe, scientists and medical professionals are developing new TMS devices that offer greater precision and effectiveness. These innovations aim to refine stimulation protocols and expand the array of brain regions targeted during treatment, ultimately improving response rates for individuals with PTSD and other mental health conditions.
Potential Applications Beyond PTSD
Below the surface, researchers are investigating TMS’s applications for a variety of mental health disorders, including anxiety, depression, and even schizophrenia. This expansion shows promise not only in treating these conditions but also in enhancing cognitive function and overall well-being.
For instance, TMS has shown potential in addressing treatment-resistant depression, which affects numerous individuals who do not respond to traditional therapies. This opens a gateway for more personalized treatment plans, allowing you to explore a broader range of options tailored specifically for your mental health needs.
Ongoing Clinical Trials
With the increasing interest in TMS, many clinical trials are currently underway to assess its effectiveness across different conditions and populations. This research aims to refine protocols and examine long-term outcomes for patients undergoing TMS treatment.
PTSD is a focal point in several ongoing clinical trials, as researchers strive to determine the optimal frequency and intensity of TMS sessions to yield the best therapeutic results. Your participation in such studies may contribute to groundbreaking discoveries that can significantly improve treatment outcomes for those suffering from trauma-related disorders.
The Future of Mental Health Treatment
One of the most exciting aspects of TMS research is its potential to transform the landscape of mental health treatment. By developing more targeted and effective therapies, TMS could offer hope to many individuals who have struggled with traditional treatment options.
A combination of TMS and other therapeutic approaches could lead to more holistic treatment strategies, integrating various modalities to address complex mental health issues. As you stay informed about advancements in this field, you may find more effective, personalized options that truly resonate with your unique experience and needs.
Summing up
On the whole, TMS offers a promising avenue for addressing PTSD by utilizing magnetic stimulation to rewire your brain after trauma. By targeting specific areas associated with anxiety and mood regulation, this non-invasive treatment can help restore balance, making it easier for you to cope with the emotional aftermath of traumatic experiences. As you explore options for healing, understanding how TMS works can empower you to make informed decisions about your mental health journey.
FAQ
Q: What is TMS and how does it work in treating PTSD?
A: TMS, or Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation, is a non-invasive treatment that uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain. For individuals with PTSD, TMS targets specific areas of the brain associated with mood regulation and emotional processing. By inducing activity in these areas, it helps to rewire the brain’s response to trauma, potentially reducing symptoms of PTSD such as anxiety, depression, and intrusive memories.
Q: How long does a typical TMS treatment session last?
A: A typical TMS session lasts between 20 to 40 minutes. During this time, the patient sits comfortably while a magnetic coil is placed on their head. The procedure is painless and does not require anesthesia. Most patients can resume their daily activities immediately after each session, as there is no significant downtime involved.
Q: How many TMS sessions are usually required for someone with PTSD?
A: The number of TMS sessions required can vary by individual but typically involves a series of 20 to 30 sessions over the course of several weeks. A treatment plan is tailored to the patient’s specific needs after an initial evaluation by a healthcare provider. Continuous assessment helps determine the effectiveness of the treatment and the need for additional sessions.
Q: Are there any side effects associated with TMS treatment?
A: TMS is generally well-tolerated, with minimal side effects. Some patients may experience mild discomfort at the site of stimulation, headache, or muscle twitching during the session. These side effects are usually temporary and resolve shortly after the treatment session ends. Serious side effects are rare, but potential patients should discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider prior to treatment.
Q: Who is a suitable candidate for TMS therapy for PTSD?
A: TMS therapy is suitable for individuals who have been diagnosed with PTSD and have not responded to traditional treatment methods such as psychotherapy or medication. It can be particularly beneficial for those seeking alternatives due to medication side effects or individuals looking to enhance their current treatment regimen. A comprehensive evaluation by a qualified mental health professional is imperative to determine if TMS is the right option for a specific individual.